Here is A list of top frequently asked SQL interview questions and answers are given below.
1. What is SQL?
Ans:
Structured Query Language is a database tool which is used to create and access database to support software application.
2. What are tables in SQL?
Ans:
The table is a collection of record and its information at a single view.
3. What are different types of statements supported by SQL?
Ans:
There are 3 types of SQL statements
- DDL (Data Definition Language): It is used to define the database structure such as tables. It includes three statements such as Create, Alter, and Drop.
Some of the DDL Commands are listed below
CREATE: It is used for creating the table.
CREATE TABLE table_name
column_name1 data_type(size),
column_name2 data_type(size),
column_name3 data_type(size),
ALTER: The ALTER table is used for modifying the existing table object in the database.
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatype
OR
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name
- DML (Data Manipulation Language): These statements are used to manipulate the data in records. Commonly used DML statements are Insert, Update, and Delete.
The Select statement is used as partial DML statement that is used to select all or relevant records in the table. - DCL (Data Control Language): These statements are used to set privileges such as Grant and Revoke database access permission to the specific user.
4. How do we use DISTINCT statement? What is its use?
Ans:
DISTINCT statement is used with the SELECT statement. If the records contain duplicate values then DISTINCT is used to select different values among duplicate records.
Syntax: SELECT DISTINCT column_name(s)
FROM table_name;
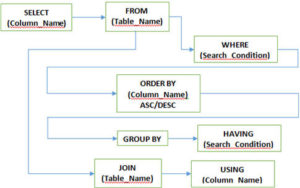
5. What are different Clauses used in SQL?
Ans:
WHERE Clause: This clause is used to define the condition, extract and display only those records which fulfill the given condition
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
GROUP BY Clause: It is used with SELECT statement to group the result of the executed query using the value specified in it. It matches the value with the column name in tables and groups the end result accordingly.
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column_name;
HAVING clause: This clause is used in association with GROUP BY clause. It is applied to the each group of result or the entire result as single group and it is much similar to WHERE clause, the only difference is you cannot use it without GROUP BY clause
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column_name
HAVING condition;
ORDER BY clause: This clause is to define the order of the query output either in ascending (ASC) or in descending (DESC) order. Ascending (ASC) is the default one but descending (DESC) is set explicitly.
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
ORDER BY column_name ASC|DESC;
USING clause: USING clause comes in use while working with SQL Joins. It is used to check equality based on columns when tables are joined. It can be used instead ON clause in Joins.
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
JOIN table_name
USING (column_name);
6. Why do we use SQL constraints? Which constraints we can use while creating database in SQL?
Ans:
Constraints are used to set the rules for all records in the table. If any constraints get violated then it can abort the action that caused it.
Constraints are defined while creating the database itself with CREATE TABLE statement or even after the table is created once with ALTER TABLE statement.
There are 5 major constraints are used in SQL, such as
NOT NULL: That indicates that the column must have some value and cannot be left null
UNIQUE: This constraint is used to ensure that each row and column has unique value and no value is being repeated in any other row or column
PRIMARY KEY: This constraint is used in association with NOT NULL and UNIQUE constraints such as on one or the combination of more than one columns to identify the particular record with a unique identity.
FOREIGN KEY: It is used to ensure the referential integrity of data in the table and also matches the value in one table with another using Primary Key
CHECK: It is used to ensure whether the value in columns fulfills the specified condition
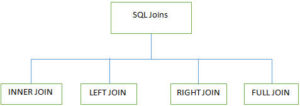
7. What are different JOINS used in SQL?
Ans:
There are 4 major types of joins made to use while working on multiple tables in SQL databases
INNER JOIN: It is also known as SIMPLE JOIN which returns all rows from BOTH tables when it has at least one column matched
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name1
INNER JOIN table_name2
ON column_name1=column_name2;
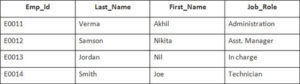
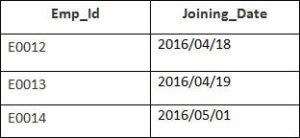
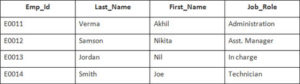
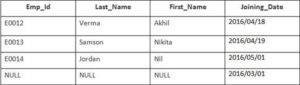
Example
In this example, we have a table Employee with the following data
Enter the following SQL statement
SELECT Employee.Emp_id, Joining.Joining_Date
FROM Employee
INNER JOIN Joining
ON Employee.Emp_id = Joining.Emp_id
ORDER BY Employee.Emp_id;
There will be 4 records selected. These are the results that you should see
Employee and orders tables where there is a matching customer_id value in both the Employee and orders tables
LEFT JOIN (LEFT OUTER JOIN): This join returns all rows from a LEFT table and its matched
rows from a RIGHT table.
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name1
LEFT JOIN table_name2
ON column_name1=column_name2;
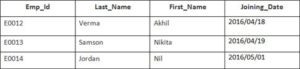
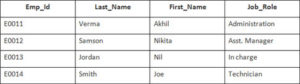
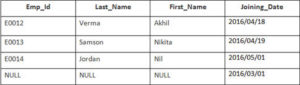
Example
In this example, we have a table Employee with the following data:
Second Table is joining
Enter the following SQL statement
SELECT Employee.Emp_id, Joining.Joining_Date
FROM Employee
LEFT OUTER JOIN Joining
ON Employee.Emp_id = Joining.Emp_id
ORDER BY Employee.Emp_id;
There will be 4 records selected. These are the results that you should see:
RIGHT JOIN (RIGHT OUTER JOIN): This joins returns all rows from the RIGHT table and its matched rows from a LEFT table.
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name1
RIGHT JOIN table_name2
ON column_name1=column_name2;
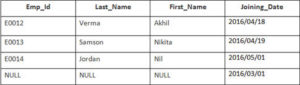
Example
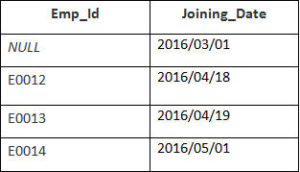
In this example, we have a table Employee with the following data
The second Table is joining
Enter the following SQL statement
SELECT Employee.Emp_id, Joining.Joining_Date
FROM Employee
LEFT OUTER JOIN Joining
ON Employee.Emp_id = Joining.Emp_id
ORDER BY Employee.Emp_id;
There will be 4 records selected. These are the results that you should see
FULL JOIN (FULL OUTER JOIN): This joins returns all when there is a match either in the RIGHT table or in the LEFT table.
Syntax: SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name1
FULL OUTER JOIN table_name2
ON column_name1=column_name2;
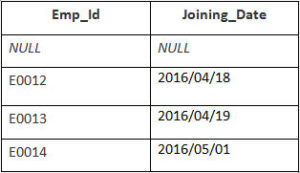
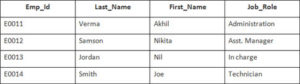
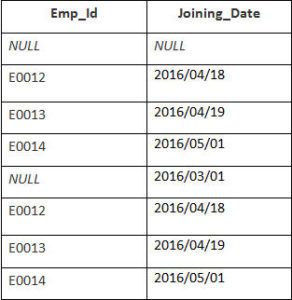
Example
In this example, we have a table Employee with the following data:
Second Table is joining
Enter the following SQL statement:
SELECT Employee.Emp_id, Joining.Joining_Date
FROM Employee
FULL OUTER JOIN Joining
ON Employee.Emp_id = Joining.Emp_id
ORDER BY Employee.Emp_id;
There will be 8 records selected. These are the results that you should see
8. What are transaction and its controls?
Ans:
A transaction can be defined as the sequence task that is performed on databases in a logical manner to gain certain results. Operations performed like Creating, updating, deleting records in the database comes from transactions.
In simple word, we can say that a transaction means a group of SQL queries executed on database records.
There are 4 transaction controls such as
COMMIT: It is used to save all changes made through the transaction
ROLLBACK: It is used to roll back the transaction such as all changes made by the transaction are reverted back and database remains as before
SET TRANSACTION: Set the name of transaction
SAVEPOINT: It is used to set the point from where the transaction is to be rolled back
9. What are properties of the transaction?
Ans:
Properties of transaction are known as ACID properties, such as
Atomicity: Ensures the completeness of all transactions performed. Checks whether every transaction is completed successfully if not then transaction is aborted at the failure point and the previous transaction is rolled back to its initial state as changes undone
Consistency: Ensures that all changes made through successful transaction are reflected properly on database
Isolation: Ensures that all transactions are performed independently and changes made by one transaction are not reflected on other
Durability: Ensures that the changes made in database with committed transactions persist as it is even after system failure
10. How many Aggregate Functions are available there in SQL?
Ans:
SQL Aggregate Functions calculates values from multiple columns in a table and returns a single value.
There are 7 aggregate functions we use in SQL
AVG(): Returns the average value from specified columns
COUNT(): Returns number of table rows
MAX(): Returns largest value among the records
MIN(): Returns smallest value among the records
SUM(): Returns the sum of specified column values
FIRST(): Returns the first value
LAST(): Returns Last value
11. What are Scalar Functions in SQL?
Ans:
Scalar Functions are used to return a single value based on the input values. Scalar Functions are as follows
UCASE(): Converts the specified field in upper case
LCASE(): Converts the specified field in lower case
MID(): Extracts and returns character from text field
FORMAT(): Specifies the display format
LEN(): Specifies the length of text field
ROUND(): Rounds up the decimal field value to a number
12. What are triggers?
Ans:
Triggers in SQL is kind of stored procedures used to create a response to a specific action performed on the table such as Insert, Update or Delete. You can invoke triggers explicitly on the table in the database.
Action and Event are two main components of SQL triggers when certain actions are performed the event occurs in response to that action.
Syntax: CREATE TRIGGER name {BEFORE|AFTER} (event [OR..]}
ON table_name [FOR [EACH] {ROW|STATEMENT}]
EXECUTE PROCEDURE functionname {arguments}
13. What is View in SQL?
Ans:
A View can be defined as a virtual table that contains rows and columns with fields from one or more table.
Syntax: CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
14. How we can update the view?
Ans:
SQL CREATE and REPLACE can be used for updating the view.
Following query syntax is to be executed to update the created view
Syntax: CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
15. Explain the working of SQL Privileges?
Ans:
SQL GRANT and REVOKE commands are used to implement privileges in SQL multiple user environments. The administrator of the database can grant or revoke privileges to or from users of database object like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, ALL etc.
GRANT Command: This command is used provide database access to user apart from an administrator.
Syntax: GRANT privilege_name
ON object_name
TO {user_name|PUBLIC|role_name}
[WITH GRANT OPTION];
In above syntax WITH GRANT OPTIONS indicates that the user can grant the access to another user too.
REVOKE Command: This command is used provide database deny or remove access to database objects.
Syntax: REVOKE privilege_name
ON object_name
FROM {user_name|PUBLIC|role_name};
16. How many types of Privileges are available in SQL?
Ans:
There are two types of privileges used in SQL, such as
System Privilege: System privileges deal with an object of a particular type and specifies the right to perform one or more actions on it which include Admin allows a user to perform administrative tasks, ALTER ANY INDEX, ALTER ANY CACHE GROUP CREATE/ALTER/DELETE TABLE, CREATE/ALTER/DELETE VIEW etc.
Object Privilege: This allows to perform actions on an object or object of another user(s) viz. table, view, indexes etc. Some of the object privileges are EXECUTE, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH, LOAD, INDEX, REFERENCES etc.
17. What is SQL Injection?
Ans:
SQL Injection is a type of database attack technique where malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field of database such that once it is executed the database is opened for an attacker. This technique is usually used for attacking Data-Driven Applications to have an access to sensitive data and perform administrative tasks on databases.
For Example: SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE condition;
18. What is SQL Sandbox in SQL Server?
Ans:
SQL Sandbox is the safe place in SQL Server Environment where untrusted scripts are executed. There are 3 types of SQL sandbox, such as
Safe Access Sandbox: Here a user can perform SQL operations such as creating stored procedures, triggers etc. but cannot have access to the memory and cannot create files.
External Access Sandbox: User can have access to files without having a right to manipulate the memory allocation.
Unsafe Access Sandbox: This contains untrusted codes where a user can have access to memory.
19. What is the difference between SQL and PL/SQL?
Ans:
SQL is a structured query language to create and access databases whereas PL/SQL comes with procedural concepts of programming languages.
20. What is the difference between SQL and MySQL?
Ans:
SQL is a structured query language that is used for manipulating and accessing the relational database, on the other hand, MySQL itself is a relational database that uses SQL as the standard database language.
21. What is the use of NVL function?
Ans:
NVL function is used to convert the null value to its actual value.
22. What is the Cartesian product of table?
Ans:
The output of Cross Join is called as a Cartesian product. It returns rows combining each row from the first table with each row of the second table. For Example, if we join two tables having 15 and 20 columns the Cartesian product of two tables will be 15×20=300 Rows.
23. What do you mean by Subquery?
Ans:
Query within another query is called as Subquery. A subquery is called inner query which returns output that is to be used by another query.
24. How many row comparison operators are used while working with a subquery?
Ans:
There are 3-row comparison operators which are used in subqueries such as IN, ANY and ALL.
25. What is the difference between clustered and non-clustered indexes?
Ans:
One table can have only one clustered index but multiple nonclustered indexes.
Clustered indexes can be read rapidly rather than non-clustered indexes.
Clustered indexes store data physically in the table or view and non-clustered indexes do not store data in table as it has separate structure from data row
26. What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE?
Ans:
The basic difference in both is DELETE is DML command and TRUNCATE is DDL
DELETE is used to delete a specific row from the table whereas TRUNCATE is used to remove all rows from the table
We can use DELETE with WHERE clause but cannot use TRUNCATE with it
27. What is the difference between DROP and TRUNCATE?
Ans:
TRUNCATE removes all rows from the table which cannot be retrieved back, DROP removes the entire table from the database and it cannot be retrieved back.
28. How to write a query to show the details of a student from Students table whose name starts with K?
Ans:
SELECT * FROM Student WHERE Student_Name like ‘K%’;
Here ‘like’ operator is used for pattern matching.
29. What is the difference between Nested Subquery and Correlated Subquery?
Ans:
Subquery within another subquery is called as Nested Subquery. If the output of a subquery is depending on column values of the parent query table then the query is called Correlated Subquery.
SELECT adminid(SELECT Firstname+’ ‘+Lastname FROM Employee WHERE
empid=emp. adminid)AS EmpAdminId FROM Employee
This query gets details of an employee from Employee table.
30. What is Normalization? How many Normalization forms are there?
Ans:
Normalization is used to organize the data in such manner that data redundancy will never occur in the database and avoid insert, update and delete anomalies.
There are Mainly 4 forms of Normalization
First Normal Form (1NF): It removes all duplicate columns from the table. Creates table for related data and identifies unique column values
Second Normal Form (2NF): Follows 1NF and creates and places data subsets in an individual table and defines relationship between tables using primary key
Third Normal Form (3NF): Follows 2NF and removes those columns which are not related through primary key
Boyce–Codd normal form (BCNF): Follows 3NF and do not define multi-valued dependencies.
31. What is Relationship? How many types of Relationship are there?
Ans:
The relationship can be defined as the connection between more than one tables in the database.
There are 4 types of relationships
- One to One Relationship
- Many to One Relationship
- Many to Many Relationship
- One to Many Relationship
32. What do you mean by Stored Procedures? How do we use it?
Ans:
A stored procedure is a collection of SQL statements which can be used as a function to access the database. We can create these stored procedures previously before using it and can execute these them wherever we require and also apply some conditional logic to it. Stored procedures are also used to reduce network traffic and improve the performance.
Syntax: CREATE Procedure Procedure_Name
(
//Parameters
)
AS
BEGIN
SQL statements in stored procedures to update/retrieve records
END
33. State some properties of Relational databases?
Ans:
In relational databases, each column should have a unique name
Sequence of rows and columns in relational databases are insignificant
All values are atomic and each row is unique
34. What are Nested Triggers?
Ans:
Triggers may implement data modification logic by using INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statement. These triggers that contain data modification logic and find other triggers for data modification are called Nested Triggers.
35. What is Cursor?
Ans:
A cursor is a database object which is used to manipulate data in a row-to-row manner.
Cursor follows steps as given below
- Declare Cursor
- Open Cursor
- Retrieve row from the Cursor
- Process the row
- Close Cursor
- Deallocate Cursor
36. What is Collation?
Ans:
Collation is set of rules that check how the data is sorted by comparing it. Such as Character data is stored using correct character sequence along with case sensitivity, type, and accent.
37. What do we need to check in Database Testing?
Ans:
Generally, in Database Testing following thing is need to be tested
- Database Connectivity
- Constraint Check
- Required Application Field and its size
- Data Retrieval and Processing With DML operations
- Stored Procedures
- Functional flow
38. What is Database White Box Testing?
Ans:
Database White Box Testing involves
Database Consistency and ACID properties
Database triggers and logical views
Decision Coverage, Condition Coverage, and Statement Coverage
Database Tables, Data Model, and Database Schema
Referential integrity rules
39. What is Database Black Box Testing?
Ans:
Database Black Box Testing involves
Data Mapping
Data stored and retrieved
Use of Black Box techniques such as Equivalence Partitioning and Boundary Value Analysis (BVA)
40. What are Indexes in SQL?
Ans:
The index can be defined as the way to retrieve the data more quickly. We can define indexes using CREATE statements.
Syntax: CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (column_name)
Further, we can also create Unique Index using following syntax;
Syntax: CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (column_name)
******************
UPDATE: Added more questions for your practice.
41. What does SQL stand for?
Ans:
SQL stands for Structured Query Language.
42. How to select all records from the table?
Ans:
To select all the records from the table we need to use the following syntax:
Select * from table_name;
43. Define join and name different types of joins?
Ans:
Join keyword is used to fetch data from related two or more tables. It returns rows where there is at least one match in both the tables included in the join. Read more here.
Type of joins are:
- Right Join
- Outer Join
- Full Join
- Cross Join
- Self Join.
44. What is the syntax to add a record to a table?
Ans:
To add a record in a table INSERT syntax is used.
Ex: INSERT into table_name VALUES (value1, value2..);
45. How do you add a column to a table?
Ans:
To add another column in the table following command has been used.
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD (column_name);
46. Define SQL Delete statement.
Ans:
Delete is used to delete a row or rows from a table based on the specified condition.
The basic syntax is as follows:
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE
47. Define COMMIT?
Ans:
COMMIT saves all changes made by DML statements.
48. What is a primary key?
Ans:
A Primary key is a column whose values uniquely identify every row in a table. Primary key values can never be reused.
49. What are foreign keys?
Ans:
When a one table’s primary key field is added to related tables in order to create the common field which relates the two tables, it called a foreign key in other tables.
Foreign Key constraints enforce referential integrity.
50. What is CHECK Constraint?
Ans:
A CHECK constraint is used to limit the values or type of data that can be stored in a column. They are used to enforce domain integrity.
51. Is it possible for a table to have more than one foreign key?
Ans:
Yes, a table can have many foreign keys and only one primary key.
52. What are the possible values for the BOOLEAN data field?
Ans:
For a BOOLEAN data field, two values are possible: -1(true) and 0(false).
53. What is a stored procedure?
Ans:
A stored procedure is a set of SQL queries which can take input and send back output.
54. What is identity in SQL?
Ans:
An identity column in the SQL automatically generates numeric values. We can define a start and increment value of identity column.
55. What is Normalization?
Ans:
The process of table design to minimize the data redundancy is called normalization. We need to divide a database into two or more table and define relationships between them.
56. What is Trigger?
Ans:
Trigger allows us to execute a batch of SQL code when a table event occurs (Insert, update or delete command executed against a specific table)
57. How to select random rows from a table?
Ans:
Using SAMPLE clause we can select random rows.
Example:
SELECT * FROM table_name SAMPLE(10);
58. Which TCP/IP port does SQL Server run?
Ans:
By default SQL Server runs on port 1433.
59. Write a SQL SELECT query that only returns each name only once from a table?
Ans:
To get the each name only once, we need to use the DISTINCT keyword.
SELECT DISTINCT name FROM table_name;
60. Explain DML and DDL?
Ans:
DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE are DML statements.
DDL stands for Data Definition Language. CREATE , ALTER, DROP, RENAME are DDL statements.
61. Can we rename a column in the output of SQL query?
Ans:
Yes using the following syntax we can do this.
SELECT column_name AS new_name FROM table_name;
62. Give the order of SQL SELECT?
Ans:
Order of SQL SELECT clauses is: SELECT, FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, ORDER BY. Only the SELECT and FROM clause are mandatory.
63. Suppose a Student column has two columns, Name and Marks. How to get name and marks of top three students.
Ans:
SELECT Name, Marks FROM Student s1 where 3 <= (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Students s2 WHERE s1.marks = s2.marks)
64. What is SQL comments?
Ans:
SQL comments can be put by two consecutive hyphens (–).
65. Difference between TRUNCATE, DELETE and DROP commands?
Ans:
DELETE removes some or all rows from a table based on the condition. It can be rolled back.
TRUNCATE removes ALL rows from a table by de-allocating the memory pages. The operation cannot be rolled back
DROP command removes a table from the database completely.
66. What are the properties of a transaction?
Ans:
Generally, these properties are referred as ACID properties. They are:
- Atomicity
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Durability.
67. What do you mean by ROWID?
Ans:
It’s an 18 character long pseudo column attached with each row of a table.
68. Define UNION, MINUS, UNION ALL, INTERSECT ?
Ans:
MINUS – returns all distinct rows selected by the first query but not by the second.
UNION – returns all distinct rows selected by either query
UNION ALL – returns all rows selected by either query, including all duplicates.
INTERSECT – returns all distinct rows selected by both queries.
69. What is a transaction?
Ans:
A transaction is a sequence of code that runs against a database. It takes the database from one consistent state to another.
70. What is the difference between UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints?
Ans:
A table can have only one PRIMARY KEY whereas there can be any number of UNIQUE keys.
The primary key cannot contain Null values whereas Unique key can contain Null values.
71. What is a composite primary key?
Ans:
Primary key created on more than one column is called composite primary key.
72. What is an Index?
Ans:
An Index is a special structure associated with a table speed up the performance of queries. The index can be created on one or more columns of a table.
73. What is the Subquery?
Ans:
A Subquery is a subset of select statements whose return values are used in filtering conditions of the main query.
74. What do you mean by query optimization?
Ans:
Query optimization is a process in which database system compares different query strategies and select the query with the least cost.
75. What is Collation?
Ans:
Set of rules that define how data is stored, how case sensitivity and Kana character can be treated etc.
76. What is Referential Integrity?
Ans:
Set of rules that restrict the values of one or more columns of the tables based on the values of the primary key or unique key of the referenced table.
77. What is Case Function?
Ans:
Case facilitates if-then-else type of logic in SQL. It evaluates a list of conditions and returns one of multiple possible result expressions.
78. Define a temp table?
Ans:
A temp table is a temporary storage structure to store the data temporarily.
79. How can we avoid duplicating records in a query?
Ans:
By using DISTINCT keyword duplicating records in a query can be avoided.
80. Explain the difference between Rename and Alias?
Ans:
Rename is a permanent name given to a table or column whereas Alias is a temporary name given to a table or column.
81. What is a View?
Ans:
A view is a virtual table which contains data from one or more tables. Views restrict data access of table by selecting only required values and make complex queries easy.
82. What are the advantages of Views?
Ans:
Advantages of Views:
Views restrict access to the data because the view can display selective columns from the table.
Views can be used to make simple queries to retrieve the results of complicated queries. For example, views can be used to query information from multiple tables without the user knowing.
83. List the various privileges that a user can grant to another user?
Ans:
SELECT, CONNECT, RESOURCES.
84. What is schema?
Ans:
A schema is a collection of database objects of a User.
85. What is Table?
Ans:
A table is the basic unit of data storage in the database management system. Table data is stored in rows and columns.
86. Do View contain Data?
Ans:
No, Views are virtual structure.
87. Can a View based on another View?
Ans:
Yes, A View is based on another View.
88. What is the difference between Having clause and Where clause?
Ans:
Both specify a search condition but Having clause is used only with the SELECT statement and typically used with GROUP BY clause.
If GROUP BY clause is not used then Having behaves like WHERE clause only.
89. What is the difference between Local and Global temporary table?
Ans:
If defined in inside a compound statement a local temporary table exists only for the duration of that statement but a global temporary table exists permanently in the DB but its rows disappear when the connection is closed.
90. What is CTE?
Ans:
A CTE or common table expression is an expression which contains temporary result set which is defined in a SQL statement.
91. What is DBMS?
Ans:
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a program that controls creation, maintenance and use of a database. DBMS can be termed as File Manager that manages data in a database rather than saving it in file systems.
92. What is RDBMS?
Ans:
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. RDBMS store the data into the collection of tables, which is related by common fields between the columns of the table. It also provides relational operators to manipulate the data stored into the tables.
93. What is SQL?
Ans:
SQL stands for Structured Query Language , and it is used to communicate with the Database. This is a standard language used to perform tasks such as retrieval, updation, insertion and deletion of data from a database.
Standard SQL Commands are Select.
94. What is a Database?
Ans:
Database is nothing but an organized form of data for easy access, storing, retrieval and managing of data. This is also known as structured form of data which can be accessed in many ways.
Example: School Management Database, Bank Management Database.
95. What are tables and Fields?
Ans:
A table is a set of data that are organized in a model with Columns and Rows. Columns can be categorized as vertical, and Rows are horizontal. A table has specified number of column called fields but can have any number of rows which is called record.
Example:
Table: Employee.
Field: Emp ID, Emp Name, Date of Birth.
Data: 201456, David, 11/15/1960.
96. What is a primary key?
Ans:
A primary key is a combination of fields which uniquely specify a row. This is a special kind of unique key, and it has implicit NOT NULL constraint. It means, Primary key values cannot be NULL.
97. What is a unique key?
Ans:
A Unique key constraint uniquely identified each record in the database. This provides uniqueness for the column or set of columns.
A Primary key constraint has automatic unique constraint defined on it. But not, in the case of Unique Key.
There can be many unique constraint defined per table, but only one Primary key constraint defined per table.
98. What is a foreign key?
Ans:
A foreign key is one table which can be related to the primary key of another table. Relationship needs to be created between two tables by referencing foreign key with the primary key of another table.
99. What is a join?
Ans:
This is a keyword used to query data from more tables based on the relationship between the fields of the tables. Keys play a major role when JOINs are used.
100. What are the types of join and explain each?
Ans:
There are various types of join which can be used to retrieve data and it depends on the relationship between tables.
Inner join.
Inner join return rows when there is at least one match of rows between the tables.
Right Join.
Right join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Right hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from the right hand side table even though there are no matches in the left hand side table.
Left Join.
Left join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Left hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from Left hand side table even though there are no matches in the Right hand side table.
Full Join.
Full join return rows when there are matching rows in any one of the tables. This means, it returns all the rows from the left hand side table and all the rows from the right hand side table.
101. What is normalization?
Ans:
Normalization is the process of minimizing redundancy and dependency by organizing fields and table of a database. The main aim of Normalization is to add, delete or modify field that can be made in a single table.
102. What is Denormalization.
Ans:
DeNormalization is a technique used to access the data from higher to lower normal forms of database. It is also process of introducing redundancy into a table by incorporating data from the related tables.
103. What are all the different normalizations?
Ans:
The normal forms can be divided into 5 forms, and they are explained below -.
First Normal Form (1NF):.
This should remove all the duplicate columns from the table. Creation of tables for the related data and identification of unique columns.
Second Normal Form (2NF):.
Meeting all requirements of the first normal form. Placing the subsets of data in separate tables and Creation of relationships between the tables using primary keys.
Third Normal Form (3NF):.
This should meet all requirements of 2NF. Removing the columns which are not dependent on primary key constraints.
Fourth Normal Form (3NF):.
Meeting all the requirements of third normal form and it should not have multi- valued dependencies.
104. What is a View?
Ans:
A view is a virtual table which consists of a subset of data contained in a table. Views are not virtually present, and it takes less space to store. View can have data of one or more tables combined, and it is depending on the relationship.
105. What is an Index?
Ans:
An index is performance tuning method of allowing faster retrieval of records from the table. An index creates an entry for each value and it will be faster to retrieve data.
106. What are all the different types of indexes?
Ans:
There are three types of indexes -.
Unique Index.
This indexing does not allow the field to have duplicate values if the column is unique indexed. Unique index can be applied automatically when primary key is defined.
Clustered Index.
This type of index reorders the physical order of the table and search based on the key values. Each table can have only one clustered index.
NonClustered Index.
NonClustered Index does not alter the physical order of the table and maintains logical order of data. Each table can have 999 nonclustered indexes.
107. What is a Cursor?
Ans:
A database Cursor is a control which enables traversal over the rows or records in the table. This can be viewed as a pointer to one row in a set of rows. Cursor is very much useful for traversing such as retrieval, addition and removal of database records.
108. What is a relationship and what are they?
Ans:
Database Relationship is defined as the connection between the tables in a database. There are various data basing relationships, and they are as follows:.
One to One Relationship.
One to Many Relationship.
Many to One Relationship.
Self-Referencing Relationship.
109. What is a query?
Ans:
A DB query is a code written in order to get the information back from the database. Query can be designed in such a way that it matched with our expectation of the result set. Simply, a question to the Database.
110. What is subquery?
Ans:
A subquery is a query within another query. The outer query is called as main query, and inner query is called subquery. SubQuery is always executed first, and the result of subquery is passed on to the main query.
111. What are the types of subquery?
Ans:
There are two types of subquery – Correlated and Non-Correlated.
A correlated subquery cannot be considered as independent query, but it can refer the column in a table listed in the FROM the list of the main query.
A Non-Correlated sub query can be considered as independent query and the output of subquery are substituted in the main query.
112. What is a stored procedure?
Ans:
Stored Procedure is a function consists of many SQL statement to access the database system. Several SQL statements are consolidated into a stored procedure and execute them whenever and wherever required.
113. What is a trigger?
Ans:
A DB trigger is a code or programs that automatically execute with response to some event on a table or view in a database. Mainly, trigger helps to maintain the integrity of the database.
Example: When a new student is added to the student database, new records should be created in the related tables like Exam, Score and Attendance tables.
114. What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE commands?
Ans:
DELETE command is used to remove rows from the table, and WHERE clause can be used for conditional set of parameters. Commit and Rollback can be performed after delete statement.
TRUNCATE removes all rows from the table. Truncate operation cannot be rolled back.
115. What are local and global variables and their differences?
Ans:
Local variables are the variables which can be used or exist inside the function. They are not known to the other functions and those variables cannot be referred or used. Variables can be created whenever that function is called.
Global variables are the variables which can be used or exist throughout the program. Same variable declared in global cannot be used in functions. Global variables cannot be created whenever that function is called.
116. What is a constraint?
Ans:
Constraint can be used to specify the limit on the data type of table. Constraint can be specified while creating or altering the table statement. Sample of constraint are.
NOT NULL.
CHECK.
DEFAULT.
UNIQUE.
PRIMARY KEY.
FOREIGN KEY.
117. What is data Integrity?
Ans:
Data Integrity defines the accuracy and consistency of data stored in a database. It can also define integrity constraints to enforce business rules on the data when it is entered into the application or database.
118. What is Auto Increment?
Ans:
Auto increment keyword allows the user to create a unique number to be generated when a new record is inserted into the table. AUTO INCREMENT keyword can be used in Oracle and IDENTITY keyword can be used in SQL SERVER.
Mostly this keyword can be used whenever PRIMARY KEY is used.
119. What is the difference between Cluster and Non-Cluster Index?
Ans:
Clustered index is used for easy retrieval of data from the database by altering the way that the records are stored. Database sorts out rows by the column which is set to be clustered index.
A nonclustered index does not alter the way it was stored but creates a complete separate object within the table. It point back to the original table rows after searching.
120. What is Datawarehouse?
Ans:
Datawarehouse is a central repository of data from multiple sources of information. Those data are consolidated, transformed and made available for the mining and online processing. Warehouse data have a subset of data called Data Marts.
121. What is Self-Join?
Ans:
Self-join is set to be query used to compare to itself. This is used to compare values in a column with other values in the same column in the same table. ALIAS ES can be used for the same table comparison.
122. What is Cross-Join?
Ans:
Cross join defines as Cartesian product where number of rows in the first table multiplied by number of rows in the second table. If suppose, WHERE clause is used in cross join then the query will work like an INNER JOIN.
123. What is user defined functions?
Ans:
User defined functions are the functions written to use that logic whenever required. It is not necessary to write the same logic several times. Instead, function can be called or executed whenever needed.
124. What are all types of user defined functions?
Ans:
Three types of user defined functions are.
Scalar Functions.
Inline Table valued functions.
Multi statement valued functions.
Scalar returns unit, variant defined the return clause. Other two types return table as a return.
125. What is collation?
Ans:
Collation is defined as set of rules that determine how character data can be sorted and compared. This can be used to compare A and, other language characters and also depends on the width of the characters.
ASCII value can be used to compare these character data.
126. What are all different types of collation sensitivity?
Ans:
Following are different types of collation sensitivity -.
Case Sensitivity – A and a and B and b.
Accent Sensitivity.
Kana Sensitivity – Japanese Kana characters.
Width Sensitivity – Single byte character and double byte character.
127. Advantages and Disadvantages of Stored Procedure?
Ans:
Stored procedure can be used as a modular programming – means create once, store and call for several times whenever required. This supports faster execution instead of executing multiple queries. This reduces network traffic and provides better security to the data.
Disadvantage is that it can be executed only in the Database and utilizes more memory in the database server.
128. What is Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)?
Ans:
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) manages transaction based applications which can be used for data entry, data retrieval and data processing. OLTP makes data management simple and efficient. Unlike OLAP systems goal of OLTP systems is serving real-time transactions.
Example – Bank Transactions on a daily basis.
129. What is CLAUSE?
Ans:
SQL clause is defined to limit the result set by providing condition to the query. This usually filters some rows from the whole set of records.
Example – Query that has WHERE condition
Query that has HAVING condition.
130. What is recursive stored procedure?
Ans:
A stored procedure which calls by itself until it reaches some boundary condition. This recursive function or procedure helps programmers to use the same set of code any number of times.
131. What is Union, minus and Interact commands?
Ans:
UNION operator is used to combine the results of two tables, and it eliminates duplicate rows from the tables.
MINUS operator is used to return rows from the first query but not from the second query. Matching records of first and second query and other rows from the first query will be displayed as a result set.
INTERSECT operator is used to return rows returned by both the queries.
132. What is an ALIAS command?
Ans:
ALIAS name can be given to a table or column. This alias name can be referred in WHERE clause to identify the table or column.
Example-
Select st.StudentID, Ex.Result from student st, Exam as Ex where st.studentID = Ex. StudentID
Here, st refers to alias name for student table and Ex refers to alias name for exam table.
133. What is the difference between TRUNCATE and DROP statements?
Ans:
TRUNCATE removes all the rows from the table, and it cannot be rolled back. DROP command removes a table from the database and operation cannot be rolled back.
134. What are aggregate and scalar functions?
Ans:
Aggregate functions are used to evaluate mathematical calculation and return single values. This can be calculated from the columns in a table. Scalar functions return a single value based on the input value.
Example -.
Aggregate – max(), count – Calculated with respect to numeric.
Scalar – UCASE(), NOW() – Calculated with respect to strings.
135. How can you create an empty table from an existing table?
Ans:
Example will be –
Select * into studentcopy from student where 1=2
Here, we are copying student table to another table with the same structure with no rows copied.
136. How to fetch common records from two tables?
Ans:
Common records result set can be achieved by –
Select studentID from student. INTERSECT Select StudentID from Exam
137. How to fetch alternate records from a table?
Ans:
Records can be fetched for both Odd and Even row numbers -.
To display even numbers-
Select studentId from (Select rowno, studentId from student) where mod(rowno,2)=0
To display odd numbers-
Select studentId from (Select rowno, studentId from student) where mod(rowno,2)=1
from (Select rowno, studentId from student) where mod(rowno,2)=1.[/sql]
138. How to select unique records from a table?
Ans:
Select unique records from a table by using DISTINCT keyword.
Select DISTINCT StudentID, StudentName from Student.
139. What is the command used to fetch first 5 characters of the string?
Ans:
There are many ways to fetch first 5 characters of the string –
Select SUBSTRING(StudentName,1,5) as studentname from student
Select RIGHT(Studentname,5) as studentname from student
140. Which operator is used in query for pattern matching?
Ans:
LIKE operator is used for pattern matching, and it can be used as -.
% – Matches zero or more characters.
_(Underscore) – Matching exactly one character.
Example –
Select * from Student where studentname like ‘a%’
Select * from Student where studentname like ‘ami_’
About the author
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.